Description
DS3800HSDD1D1F: Product Overview
The board serves as a dedicated solenoid driver module within the Speedtronic Mark IV turbine control architecture. Positioned within the control rack assembly, this unit provides the controlled current output necessary to energize solenoid valves, pilot actuators, and electromagnetic positioning devices critical to turbine hydraulic and pneumatic control systems. In the Mark IV’s triple modular redundant (TMR) system, this board operates within each independent control channel, ensuring that fuel valves, hydraulic actuators, and auxiliary solenoids respond reliably to control commands.
As a solenoid driver, the unit manages the switching of inductive loads with integrated protection against voltage transients generated when de-energizing solenoid coils. The board incorporates power transistors capable of handling the current demands of industrial solenoids, along with freewheeling diodes or equivalent suppression circuits that clamp inductive kickback to protect both the driver circuitry and the controlled devices. The eight independent channels allow simultaneous control of multiple solenoid functions—such as fuel valve pilots, hydraulic selector valves, and pneumatic control relays—from a single board position.
The board features a large connector port along the left edge that facilitates interface with external solenoid valve manifolds or junction boxes, allowing the board to be mounted in the control rack while serving field devices located on the turbine skid. Individual LEDs provide channel-by-channel status indication, allowing maintenance personnel to verify solenoid energization without requiring diagnostic software connections.
This board belongs to the DS3800 series of the Mark IV platform, deployed across heavy-duty gas turbines (Frame 3, 5, 6, 7, 9) and LM aeroderivative units. The platform’s distributed architecture allows solenoid control to execute at the rack level while maintaining deterministic synchronization with the turbine protection and sequencing logic, ensuring that fluid power systems respond within milliseconds of command generation.

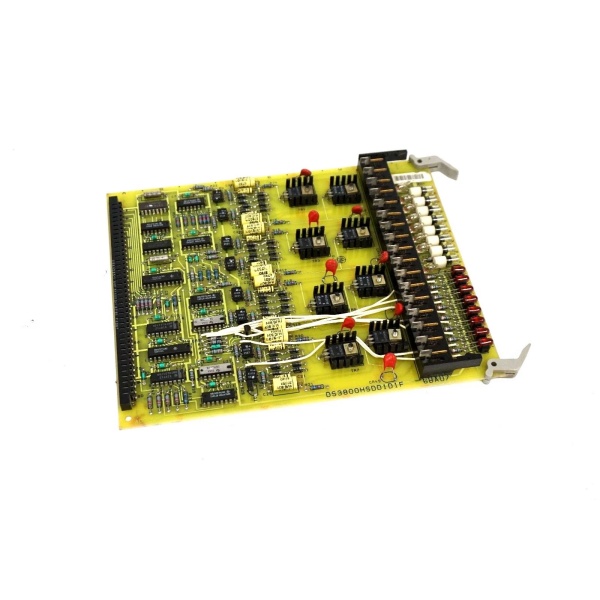
GE DS3800HSDD1D1F
DS3800HSDD1D1F: Technical Specifications
-
Model Number: DS3800HSDD1D1F
-
Manufacturer: General Electric
-
Product Type: Solenoid Driver Card
-
Series: GE Speedtronic Mark IV
-
Architecture: Triple Modular Redundant (TMR) compatible
-
Drive Channels: 8 independent solenoid drive outputs
-
Output Device: Power transistors with inductive load protection
-
Load Type: Solenoid valves, pilot actuators, electromagnetic positioners
-
Transient Protection: Integrated voltage limitation and kickback suppression diodes
-
Status Indication: 8 LEDs (one per channel) for solenoid energization status
-
External Interface: Large connector port (left edge) for field wiring interface
-
Passive Components: 8 banded resistors, yellow capacitors, rectifiers
-
Integrated Circuits: 21 ICs for drive logic and protection
-
Backplane Interface: High-density modular connector (AMD 218A4553-1 compatible)
-
Operating Temperature: -40°C to +70°C (industrial grade)
-
Storage Temperature: -40°C to +85°C
-
Humidity: 5% to 95% non-condensing
-
Vibration/Shock: 5 g vibration / 50 g shock (per Mark IV specifications)
-
Mounting: Standard Mark IV rack slot with integrated retention levers
Part 4: Core Features & Customer Value
Inductive Load Management with Integrated Protection:
The primary function of this board is to switch solenoid valves and inductive actuators while managing the high voltage transients generated when de-energizing these loads. Integrated freewheeling diodes or equivalent suppression circuitry clamp the inductive kickback that occurs when solenoid coils are turned off, protecting the output transistors from voltage spikes that could otherwise cause premature failure. This protection extends the operational life of both the driver board and the solenoid valves themselves, reducing maintenance frequency in applications where valves cycle frequently during turbine startup and loading sequences.
The primary function of this board is to switch solenoid valves and inductive actuators while managing the high voltage transients generated when de-energizing these loads. Integrated freewheeling diodes or equivalent suppression circuitry clamp the inductive kickback that occurs when solenoid coils are turned off, protecting the output transistors from voltage spikes that could otherwise cause premature failure. This protection extends the operational life of both the driver board and the solenoid valves themselves, reducing maintenance frequency in applications where valves cycle frequently during turbine startup and loading sequences.
Channel-by-Channel Status Visibility:
Eight individual LEDs provide immediate visual confirmation of which solenoids are energized at any given moment. During troubleshooting, technicians can verify that control commands are reaching the board and that specific valves are responding without requiring multimeter testing or laptop connections. This visibility is particularly valuable during hydraulic system commissioning or when diagnosing stuck valves, as it allows rapid determination of whether a fault lies in the control command, the driver output, or the field device itself.
Eight individual LEDs provide immediate visual confirmation of which solenoids are energized at any given moment. During troubleshooting, technicians can verify that control commands are reaching the board and that specific valves are responding without requiring multimeter testing or laptop connections. This visibility is particularly valuable during hydraulic system commissioning or when diagnosing stuck valves, as it allows rapid determination of whether a fault lies in the control command, the driver output, or the field device itself.
Robust External Connectivity:
The large connector port along the left edge accommodates heavy-gauge wiring necessary for solenoid current loads and facilitates connection to external terminal blocks or valve manifolds. This design allows the control electronics to remain in the protected control cabinet while serving field devices located on the hot turbine skid, reducing wiring complexity and enabling standardized cable harnesses between the control room and field equipment. The connector design ensures reliable retention despite the vibration conditions typical of turbine enclosures.
The large connector port along the left edge accommodates heavy-gauge wiring necessary for solenoid current loads and facilitates connection to external terminal blocks or valve manifolds. This design allows the control electronics to remain in the protected control cabinet while serving field devices located on the hot turbine skid, reducing wiring complexity and enabling standardized cable harnesses between the control room and field equipment. The connector design ensures reliable retention despite the vibration conditions typical of turbine enclosures.
Voltage Limitation Strategy Integration:
As part of the broader Mark Series voltage limitation architecture, this board incorporates standardized protection components that prevent overvoltage conditions from propagating through the solenoid control circuits. This systematic approach to voltage management ensures that transient suppression is coordinated across all boards in the system, preventing cumulative damage from switching events and maintaining the safety integrity of the control system over decades of operation.
As part of the broader Mark Series voltage limitation architecture, this board incorporates standardized protection components that prevent overvoltage conditions from propagating through the solenoid control circuits. This systematic approach to voltage management ensures that transient suppression is coordinated across all boards in the system, preventing cumulative damage from switching events and maintaining the safety integrity of the control system over decades of operation.
Hot-Swappable Redundancy:
The board supports replacement within the Mark IV TMR architecture, allowing technicians to restore solenoid control functionality without turbine shutdown. This capability is critical for applications where solenoid valves control fuel admission or hydraulic safety systems; failed channels can be restored quickly using spare inventory, ensuring that redundant control capability is maintained and preventing forced outages due to driver electronics failures.
The board supports replacement within the Mark IV TMR architecture, allowing technicians to restore solenoid control functionality without turbine shutdown. This capability is critical for applications where solenoid valves control fuel admission or hydraulic safety systems; failed channels can be restored quickly using spare inventory, ensuring that redundant control capability is maintained and preventing forced outages due to driver electronics failures.
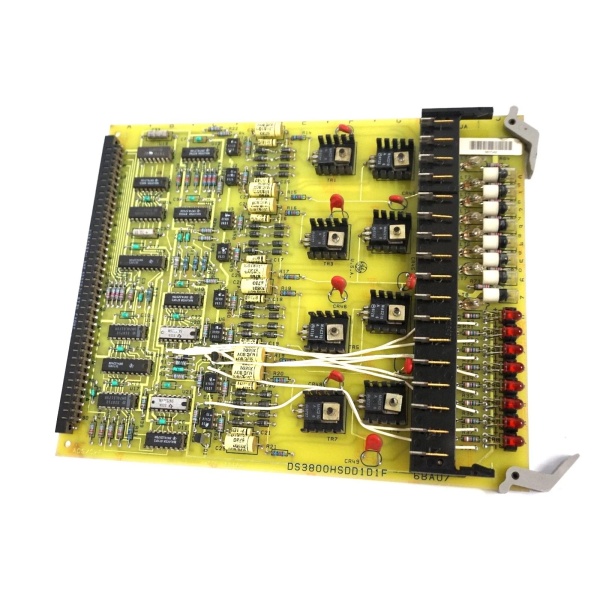
GE DS3800HSDD1D1F
Part 5: Typical Applications
Gas Turbine Fuel Valve Pilot Control:
The board is deployed in GE Frame 5, 6, and 7 gas turbines to drive the pilot solenoid valves that control main fuel valve actuation. In these applications, the eight channels typically manage stop valve solenoids, control valve pilots, and fuel transfer valve actuators that sequence the admission of natural gas or liquid fuel during startup. The inductive protection circuitry ensures reliable operation despite the frequent cycling required during turbine warm-up and fuel transfer operations, while the LED indicators allow operators to verify valve states during manual operation or emergency procedures.
The board is deployed in GE Frame 5, 6, and 7 gas turbines to drive the pilot solenoid valves that control main fuel valve actuation. In these applications, the eight channels typically manage stop valve solenoids, control valve pilots, and fuel transfer valve actuators that sequence the admission of natural gas or liquid fuel during startup. The inductive protection circuitry ensures reliable operation despite the frequent cycling required during turbine warm-up and fuel transfer operations, while the LED indicators allow operators to verify valve states during manual operation or emergency procedures.
Hydraulic Power Unit Directional Control:
In steam turbine and gas turbine hydraulic power units (HPUs), the board drives the directional control solenoids that position hydraulic valves governing steam admission, inlet guide vanes, and compressor stators. The eight independent channels allow simultaneous control of multiple hydraulic functions—such as opening the main steam admission valve while closing bypass valves—during turbine loading sequences. The robust connector interface accommodates the wiring runs between the control cabinet and hydraulic skid-mounted valve manifolds, ensuring reliable operation despite the high vibration environment near hydraulic pumps.
In steam turbine and gas turbine hydraulic power units (HPUs), the board drives the directional control solenoids that position hydraulic valves governing steam admission, inlet guide vanes, and compressor stators. The eight independent channels allow simultaneous control of multiple hydraulic functions—such as opening the main steam admission valve while closing bypass valves—during turbine loading sequences. The robust connector interface accommodates the wiring runs between the control cabinet and hydraulic skid-mounted valve manifolds, ensuring reliable operation despite the high vibration environment near hydraulic pumps.
Pneumatic Control System Actuation:
For turbine applications utilizing pneumatic actuators for bleed valves, antisurge valves, or damper controls, the board provides the 24VDC solenoid drive necessary to position these air-operated devices. The voltage limitation circuitry protects against the inductive spikes generated by pneumatic solenoids, which can be particularly severe due to the rapid cycling required for surge control or bleed valve modulation. The board’s status LEDs facilitate troubleshooting of pneumatic system faults by confirming whether control signals are reaching the solenoid pilots that operate the air valves.
For turbine applications utilizing pneumatic actuators for bleed valves, antisurge valves, or damper controls, the board provides the 24VDC solenoid drive necessary to position these air-operated devices. The voltage limitation circuitry protects against the inductive spikes generated by pneumatic solenoids, which can be particularly severe due to the rapid cycling required for surge control or bleed valve modulation. The board’s status LEDs facilitate troubleshooting of pneumatic system faults by confirming whether control signals are reaching the solenoid pilots that operate the air valves.
Aeroderivative Package Valve Control:
In LM6000 and LM2500 installations, the board manages the compact, high-density solenoid packages typical of aeroderivative fuel and hydraulic systems. The eight-channel density allows control of multiple fuel staging valves, variable geometry actuators, and compartment ventilation dampers from a single board position, conserving rack space in the limited control enclosures of these packages. The board’s vibration resistance ensures reliable operation in the higher-frequency vibration environments characteristic of high-speed aeroderivative turbines.
In LM6000 and LM2500 installations, the board manages the compact, high-density solenoid packages typical of aeroderivative fuel and hydraulic systems. The eight-channel density allows control of multiple fuel staging valves, variable geometry actuators, and compartment ventilation dampers from a single board position, conserving rack space in the limited control enclosures of these packages. The board’s vibration resistance ensures reliable operation in the higher-frequency vibration environments characteristic of high-speed aeroderivative turbines.
Emergency Shutdown and Safety Systems:
Within the Mark IV’s protection architecture, this board drives the solenoid valves that initiate emergency fuel shutoff or hydraulic system isolation when protective trips occur. The deterministic response ensures that safety solenoids de-energize within milliseconds of a trip command, closing fuel valves or venting hydraulic pressure to place the turbine in a safe state. The TMR redundancy ensures that even during single-channel maintenance, the remaining channels maintain the capability to execute emergency shutdown functions.
Within the Mark IV’s protection architecture, this board drives the solenoid valves that initiate emergency fuel shutoff or hydraulic system isolation when protective trips occur. The deterministic response ensures that safety solenoids de-energize within milliseconds of a trip command, closing fuel valves or venting hydraulic pressure to place the turbine in a safe state. The TMR redundancy ensures that even during single-channel maintenance, the remaining channels maintain the capability to execute emergency shutdown functions.



