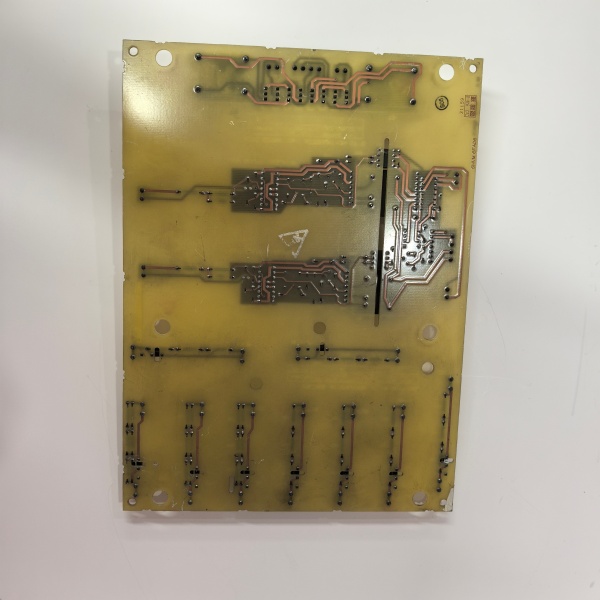
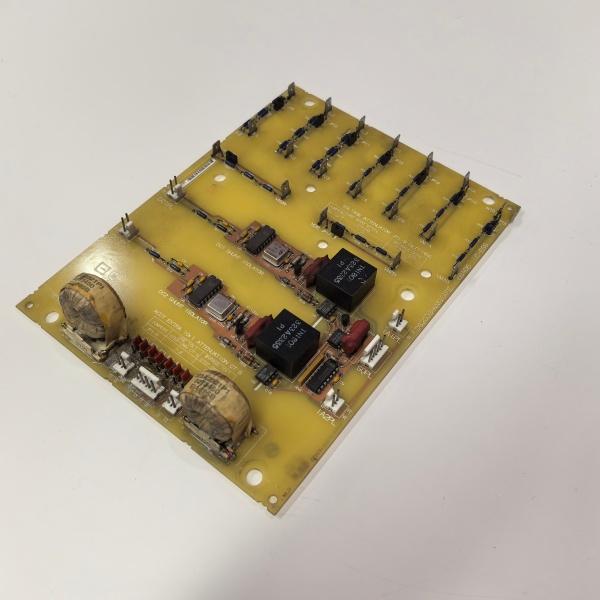
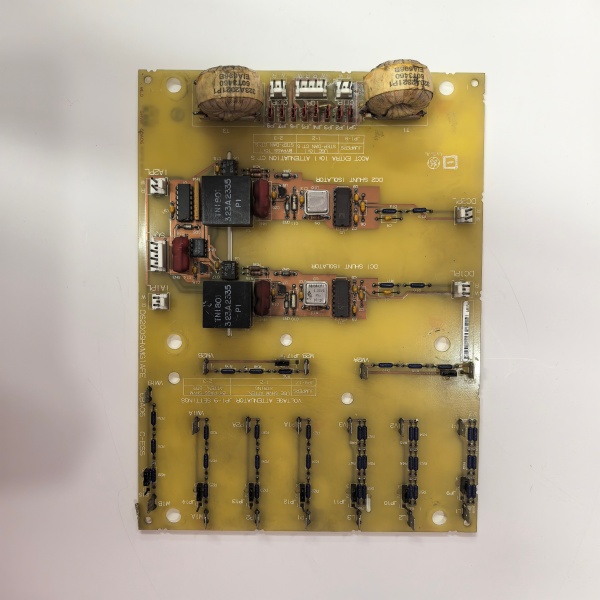
Description
Key Technical Specifications
-
Model Number: DS200SHVMG1AFE
-
Manufacturer: General Electric
-
System Voltage: ≤ 600 V AC / 800 V DC (Group 1 M-frame)
-
Current-Transformer Attenuation: 10:1 selectable via JP1-JP8 (all jumpers must be set alike)
-
Signal Conversion: Differential frequency outputs 0–500 kHz from ±500 mV shunt signals via on-board VCO
-
Gate Outputs: 6 × fiber-optic ST ports, 15 mA @ 820 nm, <1 µs channel-to-channel skew
-
Surge Protection: 40 mm metal-oxide varistors, 1 kJ pulse rating, integral with board traces
-
Isolation: 2.5 kV RMS optical on fibers, 1.5 kV card-to-ground
-
Jumpers: 17 total (attenuation, phase angle, filter corner)
-
Connectors: J1–J4 40-pin to SDCI, P1–P6 HV bayonet lugs, 6 × ST fiber
-
Operating Temperature: 0 – 60 °C board rating
-
Board Size: 250 × 220 × 40 mm; weight 2.3 kg (metal-clad frame)
-
Repairability: Non-repairable epoxy-sealed traces; replace complete board on failure
DS200SHVMG1AFE
Field Application & Problem Solved
In an EX2100 exciter the field bridge sits at 480 VAC and the control rack sits at ground. This card is the moat. It drops the 600 V line down to ±500 mV the SDCI A/D can swallow, clamps lightning hits with its 40 mm MOV string, and shoots sub-microsecond gate pulses down plastic fiber to each SCR’s gate-quench unit. When a MOV shorts it blows the on-board trace instead of the $8 k SDCI—swap time is five minutes and you’re back to full VARs. Bottom line: no SHVM, no isolated gate drive; no gate drive, no exciter; no exciter, no megawatts.
In an EX2100 exciter the field bridge sits at 480 VAC and the control rack sits at ground. This card is the moat. It drops the 600 V line down to ±500 mV the SDCI A/D can swallow, clamps lightning hits with its 40 mm MOV string, and shoots sub-microsecond gate pulses down plastic fiber to each SCR’s gate-quench unit. When a MOV shorts it blows the on-board trace instead of the $8 k SDCI—swap time is five minutes and you’re back to full VARs. Bottom line: no SHVM, no isolated gate drive; no gate drive, no exciter; no exciter, no megawatts.
Installation & Maintenance Pitfalls (Expert Tips)
JP1-JP8 must be identical
These eight jumpers select 10:1 CT attenuation. Set one differently and the SDCC sees a 20 % current imbalance and will over-fire the bridge—expect melted SCRs inside a week. Photograph the old board before you pull it.
JP1-JP8 must be identical
These eight jumpers select 10:1 CT attenuation. Set one differently and the SDCC sees a 20 % current imbalance and will over-fire the bridge—expect melted SCRs inside a week. Photograph the old board before you pull it.
Fiber bend radius is 1.5 in—no exceptions
Sharp kinks add 3 dB loss; the gate driver sees 8 mA instead of 15 and misfires. Use the orange plastic guide riveted to the bulkhead and zip-tie every 6 in.
Sharp kinks add 3 dB loss; the gate driver sees 8 mA instead of 15 and misfires. Use the orange plastic guide riveted to the bulkhead and zip-tie every 6 in.
MOV failure is resistive—ohm before power
A blown MOV reads <10 Ω line-to-ground; if you energize you’ll drag the AC bus down and fault the whole rack. Meter each input pin to chassis first thing.
A blown MOV reads <10 Ω line-to-ground; if you energize you’ll drag the AC bus down and fault the whole rack. Meter each input pin to chassis first thing.
Metal frame is live at line potential
The heat-spreader plane floats at cathode potential. Bolt it to the cabinet while the feeder is hot and you’ll strike an arc across the mounting hole. Always rack the upstream breaker before you swap the card.
The heat-spreader plane floats at cathode potential. Bolt it to the cabinet while the feeder is hot and you’ll strike an arc across the mounting hole. Always rack the upstream breaker before you swap the card.
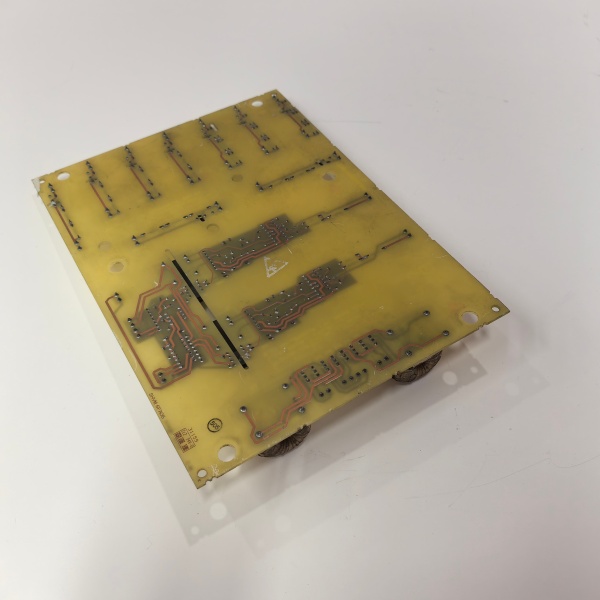

DS200SHVMG1AFE
Technical Deep Dive & Overview
Internally the board is a passive-optical hybrid. Precision resistor-dividers scale high-voltage feedback to ±500 mV; a voltage-controlled oscillator converts the shunt signal to 0–500 kHz digital pulses for noise-immune transmission to the SDCI
Internally the board is a passive-optical hybrid. Precision resistor-dividers scale high-voltage feedback to ±500 mV; a voltage-controlled oscillator converts the shunt signal to 0–500 kHz digital pulses for noise-immune transmission to the SDCI
. Six Avago HFBR-1522 transmitters turn 5 V logic edges into 820 nm light pulses; receivers on each SCR gate-quench convert back to 15 V gate current. Because everything is hardware you can hot-swap with the bridge powered—pull the old card, move fibers one-for-one, snap the 40-pin connector, and the SDCI re-acquires gate timing inside 50 ms
.