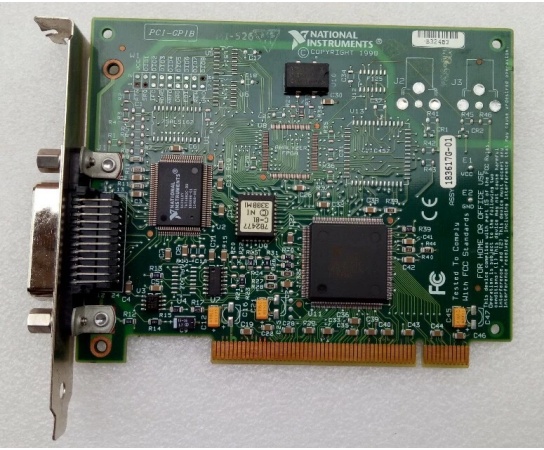
Description
Key Technical SpecificationsNI
- Model Number: PCI-GPIB
- Manufacturer: National Instruments (NI)
- Communication Standard: Fully compliant with IEEE 488.1 and IEEE 488.2 protocols
- Data Transfer Rate: Over 1.5 MB/s with IEEE 488.1 three-wire interlocked handshake; over 7.7 MB/s with high-speed HS488 non-interlocked handshake
- Bus Interface: 32-bit PCI bus, Plug-and-Play compatible
- Data Transfer Mode: Onboard bus master DMA controller, avoiding microprocessor interruptions during data transmission
- Connector: 24-Pin Female GPIB (IEEE 488) connector
- Max Connected Devices: Supports up to 15 GPIB instruments in a single bus system
- Software Compatibility: Compatible with NI-488.2 driver, NI-VISA driver, LabVIEW, LabWindows/CVI, C/C++, Python; supports Linux and Windows operating systems
- Operating Temperature: 0°C to 55°C (typical industrial and laboratory operating range)
- Power Consumption: Powered by PCI bus, low power consumption (typical 5W, maximum 8W), no additional power supply required
Field Application & Problem Solved
The NI PCI-GPIB solves these problems by acting as a bridge between PCI-equipped computers and GPIB instruments. It is widely used in electronic manufacturing factories for automated testing of circuit boards—connecting multiple test instruments to a computer to realize automated data collection and analysis. In aerospace research labs, it controls sensors and measuring equipment in environmental test chambers to synchronize data transmission. It also plays a key role in university scientific research laboratories, helping researchers integrate various GPIB-based experimental instruments for precise experimental control.
Its core value lies in its high compatibility and stable transmission performance. It unifies the control of multiple types of GPIB instruments, replacing manual operation and improving test efficiency and data accuracy. For test engineers, it integrates seamlessly with NI software, enabling rapid development of automated test procedures without complicated low-level programming.
Installation & Maintenance Pitfalls (Expert Tips)
- Missing Critical Driver Installation: The card relies on NI-488.2 and NI-VISA drivers to function. Installing only the operating system’s default drivers results in failure to recognize the card or inability to communicate with instruments. A university lab failed to connect a GPIB multimeter until it installed the matching NI-488.2 driver after initially using only generic PCI drivers. Always install the latest version of the dedicated drivers from NI’s official website.
- Incorrect Instrument Address Conflict: Each GPIB instrument on the bus needs a unique address (0 – 30). If two instruments share the same address, the card cannot distinguish between them, causing communication timeouts. When connecting multiple instruments, use NI MAX software to scan and confirm addresses. An electronics factory encountered intermittent communication failures; the root cause was two spectrum analyzers both set to address 5.
- Ignoring GPIB Bus Cable Length Limits: The total length of the GPIB bus cable should not exceed 20 meters. Excessively long cables or daisy – chaining too many extension cables lead to signal attenuation and data transmission errors. A research institute’s temperature test system had data loss issues when using a 30 – meter cable. Replacing it with a 15 – meter shielded GPIB cable restored stable transmission.
- Forgetting to Close MAX Before Running Test Programs: Keeping the NI MAX test panel open while running LabVIEW or C++ test programs causes resource access conflicts, resulting in program crashes or communication failures. Remember to close the MAX software after configuring the device. A semiconductor test team once spent 2 hours troubleshooting a program crash, only to find it was due to the MAX test panel remaining open.

NI PCI-GPIB
Technical Deep Dive & Overview
The onboard bus master DMA controller is a key design highlight. Unlike conventional PIO data transfer that occupies CPU resources, DMA directly transmits data between the card and the computer’s memory. This not only improves transmission efficiency but also prevents the CPU from being overwhelmed by data transfer tasks, ensuring the stable operation of other test software and system processes simultaneously.
In terms of protocol compatibility, its support for IEEE 488.2 means it can recognize and execute standardized commands from various GPIB instruments, enhancing compatibility with third – party devices. The 24 – pin GPIB connector follows industry standards, ensuring universal connection with GPIB cables and instruments from different manufacturers.
Although the PCI bus is relatively traditional, it is still widely present in industrial computers and laboratory workstations. The PCI-GPIB fully leverages the stability of the PCI bus to provide long – term reliable operation in harsh industrial environments and long – term laboratory tests. While newer PCIe-GPIB cards have emerged, the PCI-GPIB remains a cost-effective and reliable choice for systems relying on PCI slots, maintaining its important position in legacy test systems and medium – speed instrument control scenarios.