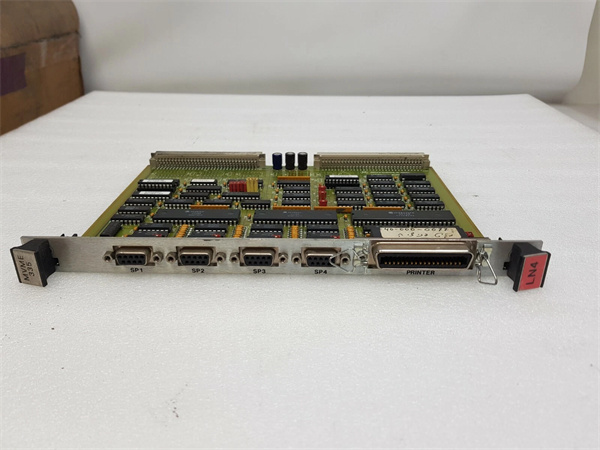
Description
Detailed Parameter Table
| Parameter Name | Parameter Value |
| Product Model | Motorola MVME335 |
| Manufacturer | Motorola (now part of Emerson’s industrial automation portfolio) |
| Product Category | VMEbus Multi-Protocol Communication Interface Module (RS-232/RS-422/RS-485 + CAN bus dual-mode) |
| Interface Configuration | 4x serial ports (software-selectable as RS-232/RS-422/RS-485); 2x CAN bus ports (CAN 2.0A/B compliant, high-speed 1 Mbps); 8x digital I/O channels (4 input, 4 output, TTL/CMOS compatible) |
| Serial Port Specifications | Baud rate: 300 bps – 230.4 kbps (software-configurable); data bits: 7/8; parity: none/even/odd; stop bits: 1/2; RS-485 max transmission distance: 1200 m, multi-drop (32 nodes/port) |
| CAN Bus Specifications | Bit rate: 10 kbps – 1 Mbps (software-configurable); frame format: standard (11-bit ID)/extended (29-bit ID); error detection: CRC, bit stuffing, bus-off recovery |
| Digital I/O Specifications | Input voltage range: 0–0.8 VDC (LOW), 2.0–5.5 VDC (HIGH); input current: 8 µA max per channel; output current: 15 mA sink/source per channel |
| Bus Standard | VMEbus (PICMG VME 1.4 compliant) – 16-bit address/data bus; slave-only mode; supports VMEbus interrupts (level 2–6) |
| Physical Dimensions | Standard 3U VME form factor (100 mm × 160 mm × 16 mm; L×W×H) – fits standard VME chassis slots |
| Power Requirements | +5 VDC (1.0 A typical, 1.5 A maximum); +12 VDC (0.3 A typical); -12 VDC (0.2 A typical); passive heat dissipation (no fan) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -10°C – 70°C (-14°F – 158°F) (extended industrial environmental tolerance) |
| Product Status | Obsolete (discontinued by manufacturer; supported via aftermarket/refurbished services) |
| Compliance Standards | VMEbus 1.4; EIA/TIA-232/422/485; ISO 11898-2 (CAN bus); FCC Class A (EMI); CE Mark; RoHS; IEC 61000-6-2/-4 (industrial EMC immunity/susceptibility) |
| Compatibility | Optimized for Motorola VME SBCs (MVME5500, MVME2434, MVME172-263/260); works with power modules (FAB 0340-1049, 01-W3324F)、communication modules (FLN4234A, MVME712/M)、I/O modules (MVME333-2, MVME162-223) |
| On-Board Features | Per-port status LEDs (serial: TX/RX/error; CAN: bus active/error; digital I/O: state); serial/CAN surge protection (2 kV ESD); digital I/O overcurrent protection (25 mA per channel); EEPROM for configuration storage; CAN bus termination (120Ω selectable) |
MOTOROLA MVME335
Product Introduction
The Motorola MVME335 is a versatile VMEbus multi-protocol communication interface module, engineered to integrate serial (RS-232/RS-422/RS-485) and CAN bus communication with discrete digital I/O—filling the gap between single-protocol modules (e.g., MVME333-2’s serial-only focus) and complex communication gateways. As a 3U VME form factor device, it is designed for industrial systems that require simultaneous connectivity to legacy serial devices (e.g., sensors, HMIs) and modern CAN-based equipment (e.g., automotive ECUs, industrial robots), eliminating the need for 2–3 separate modules and saving critical VME chassis slots.
A defining strength of the MVME335 is its seamless integration with the Motorola VME ecosystem. When paired with a host SBC like the MVME5500, it leverages the VMEbus to receive configuration commands (e.g., serial baud rate, CAN bit rate, digital I/O direction) and transmit multi-protocol data—such as RS-485 sensor readings, CAN bus robot status, and local digital I/O states. It draws stable power from modules like the FAB 0340-1049 (via VME backplane) or 01-W3324F (for auxiliary power), while its -10°C–70°C temperature range expands reliability beyond standard industrial modules (e.g., MVME333-2’s 0°C–60°C)—suitable for cold storage facilities or hot factory floors.
Whether deployed in automotive manufacturing、industrial robot control, or hybrid legacy-modern systems, the MVME335 enables streamlined multi-device communication. Its CAN bus support (1 Mbps high-speed) meets the real-time requirements of motion control, while serial ports retain compatibility with thousands of legacy devices—making it a cost-effective, future-proof solution for legacy VME systems undergoing gradual modernization.
Core Advantages and Technical Highlights
Multi-Protocol Integration for Hybrid System Connectivity
The MVME335’s combination of 4x flexible serial ports, 2x CAN bus ports, and 8x digital I/O channels eliminates the need for separate serial, CAN, and I/O modules—reducing VME chassis slot usage by up to 66%. For example, in an automotive assembly line, the module can: 1) use 2x RS-485 ports to connect 32 remote torque sensors (monitoring bolt tightness), 2) use 2x CAN bus ports to link to 10 robotic arms (transmitting motion commands), 3) use 4x digital inputs to monitor safety interlocks, and 4) use 4x digital outputs to activate emergency stops. This integrated design simplifies wiring, reduces communication latency between protocols, and lowers overall system cost compared to mixed single-protocol modules.
High-Speed CAN Bus for Real-Time Motion Control
The MVME335’s 2x CAN bus ports (CAN 2.0A/B compliant, 1 Mbps max bit rate) meet the real-time requirements of industrial motion control—critical for applications like robotic assembly or conveyor synchronization. Unlike serial protocols (e.g., RS-485) with variable latency, CAN bus uses priority-based messaging, ensuring time-sensitive commands (e.g., robot gripper actuation) are transmitted before non-critical data (e.g., status updates). In a packaging machine with 5 CAN-based servo motors, the module can synchronize motor speeds via CAN bus, achieving ±1 ms timing accuracy—far better than RS-485’s ±10 ms latency. The selectable 120Ω termination also simplifies bus design, avoiding signal reflections in long CAN networks.
Extended Environmental Tolerance and Robust Protection
With an operating temperature range of -10°C–70°C (vs. MVME333-2’s 0°C–60°C), the MVME335 operates reliably in extreme industrial environments—from -5°C cold-chain food processing facilities to 65°C automotive paint shops. Its 2 kV ESD surge protection (double MVME333-2’s 1 kV) safeguards serial and CAN ports against electrical interference from nearby welding equipment or power tools. For instance, in a steel mill, the module’s surge protection prevents CAN bus port damage from arc welding-induced voltage spikes, while overcurrent protection on digital I/O channels shields against short circuits from water ingress—minimizing unplanned downtime.
Flexible Serial Configuration for Legacy Compatibility
The MVME335’s 4x serial ports support software-selectable RS-232/RS-422/RS-485 modes and baud rates up to 230.4 kbps (faster than MVME333-2’s 115.2 kbps)—enabling compatibility with both legacy and modern serial devices. For example, in a manufacturing plant with older RS-232 HMIs (9600 bps) and new RS-485 sensors (230.4 kbps), the module can configure each port independently via the MVME2434 SBC, avoiding the need to replace legacy HMIs. The EEPROM storage of configuration parameters also ensures settings are retained during power cycles, eliminating reconfiguration after downtime—critical for 24/7 production lines.
Typical Application Scenarios
Automotive Manufacturing Robot Control
In an automotive body welding line, the MVME335 (paired with MVME5500 SBC) coordinates multi-protocol communication: 2x CAN bus ports connect to 8 welding robots (transmitting motion commands and receiving position feedback at 1 Mbps), 2x RS-485 ports link to 24 torque sensors (monitoring weld bolt tightness), 4x digital inputs monitor safety light curtains, and 4x digital outputs activate robot lockouts. The module’s CAN bus real-time performance ensures robots synchronize their welding sequences (±1 ms accuracy), while RS-485 multi-drop reduces wiring complexity. Its -10°C–70°C range withstands the line’s temperature fluctuations, and surge protection prevents damage from welding EMI.
Industrial Conveyor Synchronization
In a logistics warehouse with 10 CAN-based conveyors, the MVME335 (paired with MVME172-263/260 SBC) manages multi-device coordination: 1x CAN bus port connects to the conveyor network (synchronizing speed and direction), 1x CAN port links to a FLN4234A communication module (transmitting data to a central WMS), 2x RS-232 ports connect to local HMIs (for operator control), and 8x digital I/O channels monitor conveyor jam sensors/activate alarms. The module’s CAN bus priority messaging ensures jam alerts are transmitted before speed commands, avoiding collisions. Its passive cooling design fits in the warehouse’s enclosed control cabinets, and ESD protection safeguards against static discharge from packaging materials.
Hybrid Legacy-Modern System in Food Processing
In a food processing plant upgrading from legacy to modern equipment, the MVME335 (paired with MVME2434 SBC) bridges old and new: 2x RS-232 ports connect to legacy PLCs (controlling older mixers), 2x RS-485 ports link to new temperature sensors (monitoring cooking tanks), 2x CAN bus ports connect to modern packaging robots, and 8x digital I/O channels control valve actuators. The module’s multi-protocol support eliminates the need for a separate CAN gateway, while its -10°C range withstands the plant’s refrigerated prep areas. The MVME712/M transmits combined data to a SCADA system, enabling unified monitoring of legacy and modern equipment.
MOTOROLA MVME335
Related Model Recommendations
Motorola MVME5500: VME SBC. Host controller for MVME335; configures serial/CAN ports and digital I/O, processes multi-protocol data, and executes control logic—critical for leveraging the module’s multi-functionality.
Motorola FAB 0340-1049: Power supply module. Primary power source for MVME335; delivers stable +5 VDC (1.5 A max), ±12 VDC to support the module’s serial/CAN and digital I/O circuits.
Motorola FLN4234A: Communication expansion module. Complements MVME335 in large systems; the FLN4234A’s 4x Ethernet ports extend the MVME335’s CAN/serial data to remote SCADA/cloud platforms.
Motorola 01-W3324F: Power distribution terminal block. Supplies auxiliary power to MVME335 (if VME backplane power is insufficient) and distributes 24V DC to connected digital I/O devices (e.g., sensors, alarms).
Motorola MVME333-2: Serial + digital I/O module. Expands the MVME335’s serial capacity; adds 2x RS-485 ports for systems needing more legacy serial connections (e.g., older sensor networks).
Phoenix Contact CAN Bus Repeater: Signal booster. Extends the MVME335’s CAN bus transmission distance beyond 40 m (max for 1 Mbps) and increases node count to 64—ideal for large conveyor networks.
Emerson RSTi-EP CAN/Ethernet Gateway: Modern gateway. Enables the MVME335’s CAN bus data to integrate with Ethernet networks (e.g., PROFINET, Ethernet/IP) for users modernizing to Industry 4.0 systems.
Installation, Commissioning and Maintenance Instructions
Installation Preparation
Before installing MVME335, power off the VME chassis and disconnect the FAB 0340-1049 power supply to prevent electrical shock. Verify the chassis has an available 3U VME slot and that the VME backplane supports 16-bit slave modules. Use an anti-static wristband and mat to protect the module’s serial/CAN and digital I/O components from ESD damage. Gather tools: Phillips-head screwdriver (for chassis mounting), twisted-pair cables (RS-422/RS-485/CAN, 22–18 AWG), 22–18 AWG wires (digital I/O), torque wrench (0.5–0.8 N·m for terminals), CAN bus termination resistors (120Ω, if needed), and a multimeter (to test signal levels). Avoid installing near high-voltage equipment (e.g., transformers) or heat sources (e.g., power resistors) to prevent EMI or thermal damage.
Commissioning and Maintenance
For commissioning, insert the MVME335 into the VME slot and secure it. Wire serial devices (RS-232: TX/RX/GND; RS-422/RS-485: A/B/GND) and CAN bus devices (H/L/GND), ensuring correct polarity (A to A, B to B for RS-485; H to H, L to L for CAN) and adding 120Ω termination at bus endpoints. Connect digital I/O devices to terminals, matching TTL/CMOS levels. Power on the FAB 0340-1049 and 01-W3324F (if used), then check LEDs: green “POWER” confirms voltage; serial/CAN “TX/RX” (blinking) indicates data; digital I/O “HIGH” (green)/“ACTIVE” (red) confirms state. Use the MVME5500’s configuration software to set serial modes/baud rates, CAN bit rates (e.g., 500 kbps for motion control), and digital I/O direction. Test communication: send serial test data to a remote device, transmit CAN messages to a robot, and toggle digital outputs to verify actuator response.
For maintenance: Inspect wiring monthly—tighten loose terminals, replace damaged cables, and clean CAN bus connectors (to prevent signal degradation). Clean the module quarterly with compressed air (low pressure) to remove dust from the VME connector and heatsink. Test surge protection semi-annually using an ESD simulator (ensure 2 kV protection). If a CAN port fails, reconfigure a spare serial port for critical legacy devices; if digital I/O malfunctions, isolate the issue with a bench power supply. When upgrading, replicate the module’s protocol configurations to avoid disrupting connected devices—use EEPROM backup to transfer settings to a new unit.
Service and Guarantee Commitment
Though Motorola MVME335 is obsolete, we offer a 90-day warranty on all refurbished units—covering defects in serial/CAN port functionality, digital I/O performance, surge protection, and LED indicators. Each refurbished module undergoes rigorous testing: 24-hour CAN bus data transfer (1 Mbps, zero packet loss), serial protocol validation (300 bps–230.4 kbps), digital I/O cycling (overcurrent protection test), and ESD surge testing (2 kV). This guarantees compliance with original industrial-grade standards.
Our technical support team (24/7 availability) provides guidance on MVME335 installation、CAN bus network design (e.g., termination, node spacing), and integration with VME SBCs like the MVME5500 or MVME2434. We offer customized maintenance plans: quarterly remote CAN bus health checks (via FLN4234A) and semi-annual on-site inspections (testing wiring, verifying surge protection). Our spare parts inventory includes critical components (e.g., CAN transceivers, serial port chips) for fast repairs—minimizing downtime in multi-protocol systems.
For users modernizing to Ethernet-based systems, we provide free consultation to select Emerson’s RSTi-EP CAN/Ethernet gateways





