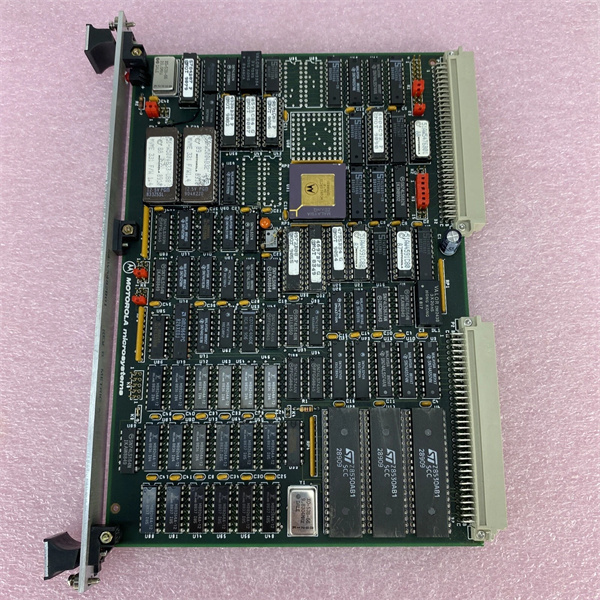
Description
Detailed Parameter Table
| Parameter name | Parameter value |
| Product model | Motorola MVME – 330 |
| Manufacturer | Motorola |
| Product category | VME Ethernet Controller (Single – slot VMEbus board) |
| Microprocessor | 10 MHz MC68000 Microprocessor Unit (MPU) |
| Input Power | 89 – 280 VAC |
| Memory | 128 k – byte dual – access RAM with parity and no wait states; 32 k – byte EROM (2 sockets) |
| Ethernet Controller | Local Area Network Controller for Ethernet (LANCE); Supports CSMA/CD protocol |
| Node Address | Node address PROM contains a unique address issued by Xerox Corp. |
| Timer Interrupt | 2ms timer interrupts the MPU for protocol software timing |
| Interface | VMEbus (IEEE P1014) A24:D16 master and slave interface for host – to – MVME – 330 communications; Serial Interface Adaptor (SIA) with Manchester encoding/decoding and transceiver cable interface; VMEbus requester, VMEbus interrupter with programmable vector, VMEbus onboard processor interrupter |
| Dimensions | 263 × 58 × 28 mm |
| Weight | 4.3 kg |
| Product Life Cycle Status | Discontinued / Obsolete |
Motorola MVME-331
Product Introduction
The Motorola MVME – 330 is a VME Ethernet Controller, designed as a single – slot VMEbus board. It plays a crucial role in enabling Ethernet communication within VME – based industrial and embedded systems. Different from some other modules that might focus on general – purpose processing or extensive I/O capabilities, the MVME – 330’s core function is to bridge the gap between VMEbus systems and Ethernet networks, facilitating data transfer and communication.
In industrial control setups, the MVME – 330 can be integrated into a VME – based control system. For example, in a large – scale industrial automation system where multiple VME – based subsystems need to communicate with each other over an Ethernet network or with external monitoring and control stations. The MVME – 330 allows these subsystems to send and receive data packets over the Ethernet, ensuring seamless communication between different parts of the system. It can also be used in scenarios where real – time data transfer from VME – connected sensors and actuators to a remote control center via Ethernet is required, such as in a power grid monitoring system.
Core Advantages and Technical Highlights
Powerful MC68000 – based Processing for Network Tasks: Equipped with a 10 MHz MC68000 Microprocessor Unit (MPU), the MVME – 330 can efficiently handle network – related processing tasks. The MC68000 is a well – known and reliable processor architecture. It can manage Ethernet protocol processing, data buffering, and transfer operations in real – time. For instance, in a factory’s network – connected control system, it can quickly process incoming Ethernet packets from various sensors and forward the relevant data to the appropriate VME – based controllers. This ensures that the control system can respond promptly to changes in the production environment.
Dual – access RAM and EROM for Data Management: The 128 k – byte dual – access RAM with parity and no wait states, along with 32 k – byte EROM (2 sockets), provides a stable and efficient memory configuration for the MVME – 330. The dual – access RAM allows for quick data access during network operations, reducing latency in data transfer. The EROM can store essential system software and configuration data, ensuring that the module can start up and function correctly even in the event of a power cycle. In a network – intensive industrial application like a large – scale logistics warehouse’s automated sorting system, the reliable memory configuration of the MVME – 330 helps in seamless data handling and system operation.
Advanced Ethernet Connectivity Features: The Local Area Network Controller for Ethernet (LANCE) in the MVME – 330 supports the CSMA/CD (Carrier – Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) protocol, which is a fundamental and reliable protocol for Ethernet communication. The module also has a unique node address stored in its PROM, issued by Xerox Corp., ensuring proper identification on the network. The 2ms timer interrupt for protocol software timing enables precise control of network operations. In a multi – module VME – based network setup, such as in a multi – building industrial complex where different VME – based control systems need to communicate over Ethernet, the MVME – 330’s advanced Ethernet features ensure stable and accurate data transfer.
Typical Application Scenarios
In industrial automation plants, the Motorola MVME – 330 can be used to connect VME – based control systems to an Ethernet network. For example, in an automotive manufacturing plant, multiple VME – based robots and conveyor systems need to communicate with a central control room. The MVME – 330 enables these VME – based subsystems to send real – time data about their operation status, such as robot arm positions, conveyor speeds, and product quality inspection results, over the Ethernet network to the central control room. This allows operators to monitor and control the entire production process from a central location.
Power generation and distribution facilities also benefit from the MVME – 330. In a power plant, various VME – connected sensors and control units need to communicate with each other and with remote monitoring stations. The MVME – 330 can be used to establish an Ethernet connection, enabling the transfer of data such as generator performance data, grid voltage and frequency measurements, and equipment status information. This helps in ensuring the stable operation of the power grid and enables remote troubleshooting and maintenance.
For large – scale data – collection and monitoring systems in industries like environmental monitoring or oil and gas exploration, the MVME – 330 can be used to connect VME – based data – acquisition modules to an Ethernet network. In an environmental monitoring network spread across a large area, VME – based modules connected to sensors for temperature, humidity, air quality, etc., can use the MVME – 330 to send collected data over Ethernet to a central data – processing center. This enables real – time monitoring and analysis of environmental conditions.
Related Model Recommendations
Motorola MVME – 331: While the MVME – 330 focuses on Ethernet communication within VME – based systems, the MVME – 331 is a microprocessor – based module with a PowerPC™ series processor. In some complex industrial systems, the MVME – 330 can be used to handle the network communication part, while the MVME – 331 can be responsible for more complex data processing and control tasks. For example, in a high – end industrial control system, the MVME – 330 can bring in data from external networks, and the MVME – 331 can analyze and act on this data.
Other VME – compatible Ethernet Controller Modules: There are other VME – compatible Ethernet controller modules available in the market. These can be considered as alternatives depending on specific requirements. For instance, if the application requires a different form factor, higher – speed Ethernet support, or additional network features, other modules might be more suitable. However, the MVME – 330’s established reputation in legacy VME – based systems makes it a reliable choice for existing installations.
General – purpose Network Interface Cards (NICs) with VME Interface Adapters: In some cases, general – purpose network interface cards with VME interface adapters can be used as substitutes. These can offer more flexibility in terms of network protocols and interface options. But they might require more complex integration and configuration compared to the dedicated MVME – 330.

Motorola MVME-331
Installation, Commissioning and Maintenance Instructions
Installation preparation: Before installing the Motorola MVME – 330, make sure the VMEbus chassis has an available single – slot and is compatible with the MVME – 330’s form factor. Check the input power supply to ensure it can provide the required 89 – 280 VAC. Use an anti – static wristband to protect the module from electrostatic discharge during handling. Gather tools such as a screwdriver for chassis mounting. Also, ensure that the Ethernet network infrastructure is properly set up, including the availability of network cables and switches.
Commissioning: After installation, power on the system. Use a compatible programming device or software to configure the MVME – 330. This may involve setting up the network parameters such as IP address, subnet mask, and gateway. Initialize the memory and load the necessary network – related software. Test the Ethernet connectivity by sending and receiving test packets. Check the module’s status LEDs (if available) to ensure proper operation.
Maintenance suggestions: Regularly check the system logs for any error messages related to the MVME – 330’s network operations. Monitor the network traffic to detect any abnormal behavior, such as excessive packet loss or high latency. Clean the module’s exterior periodically to remove dust, which can affect its performance. Since it is a discontinued product, it is advisable to have spare modules in stock in case of failure. Store spare modules in an anti – static environment. If there are any issues with network connectivity, check the network cables, switches, and the MVME – 330’s configuration settings.
Service and Guarantee Commitment
As a discontinued product, the standard factory warranty is no longer applicable. However, some third – party service providers may offer repair services for the Motorola MVME – 330. These providers may have access to spare parts and the technical expertise to fix common issues such as network controller failures, memory problems, or interface malfunctions.
Users are recommended to search for specialized legacy system support companies. These companies often maintain archives of technical documentation for discontinued products like the MVME – 330. They can provide valuable information on troubleshooting, repair procedures, and even offer limited – time support contracts for critical applications. Although the MVME – 330 is discontinued, with proper support, it can still be used in legacy VME – based systems for a certain period, helping users avoid the high cost of a full – scale system replacement.