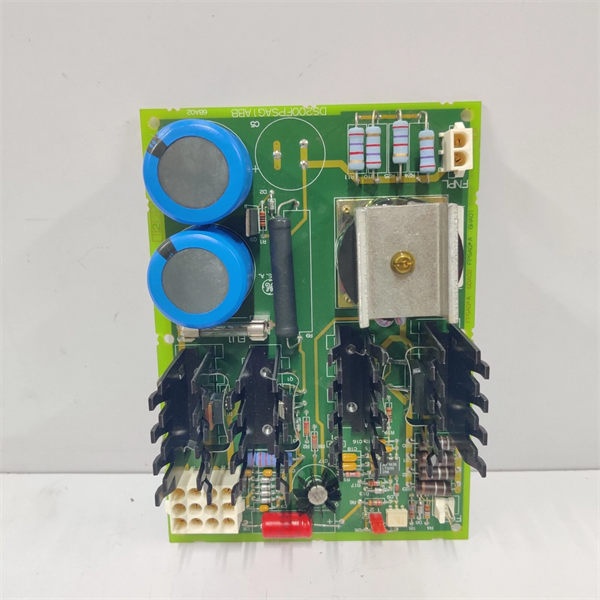
Description
Key Technical Specifications
-
Model Number: DS200TBQDG1AFE
-
Manufacturer: General Electric
-
Max System Voltage: 4500 Vpk (AC & DC)
-
Gate Output: 2 × 6 fiber-optic ST ports, 15 mA peak @ 820 nm
-
Isolation: 2.5 kV optical, 1500 V copper-to-ground
-
Snubbers: AC & DC RC networks, 0.1 µF / 100 Ω, 1 kW pulse
-
Feedback Inputs: 8 differential ±10 V (bridge volts, armature current)
-
Connectors: J1–J4 40-pin to SDCC back-plane; P1–P6 HV bayonet
-
Power Demand: +5 V @ 0.8 A, +15 V @ 0.2 A from rack
-
Temperature Range: –20 °C to +70 °C
-
Board Size: 279 × 216 × 25 mm, 1.1 kg conformal-coated
-
MTBF: >200 kH @ 40 °C (MIL-HDBK-217F)
DS200FPSAG1ABB
Field Application & Problem Solved
A 9E gas-turbine static-start DC link runs 3 200 A through a six-pulse SCR bridge. The bridge sits at 2 800 Vdc; the control rack sits at ground. You can’t run copper gate wires down the hall—this card does the lift. It lives in the high-voltage cabinet, receives 5 V logic pulses from the SDCC, and shoots them down 2 m plastic fiber to each SCR’s gate-quench unit. At the same time it scales the 2 800 V bridge voltage and 3 kA current down to ±10 V and ships it back to the SDCC over differential pairs. If one SCR fails to commutate, the board’s dv/dt comparator flags “SHVI FAULT” within 2 µs and the Mark V blocks the next pulse—saving you from a diode explosion and a week-long outage. Bottom line: without the SHVI you can’t safely close the 2 kV gap between silicon and software.
A 9E gas-turbine static-start DC link runs 3 200 A through a six-pulse SCR bridge. The bridge sits at 2 800 Vdc; the control rack sits at ground. You can’t run copper gate wires down the hall—this card does the lift. It lives in the high-voltage cabinet, receives 5 V logic pulses from the SDCC, and shoots them down 2 m plastic fiber to each SCR’s gate-quench unit. At the same time it scales the 2 800 V bridge voltage and 3 kA current down to ±10 V and ships it back to the SDCC over differential pairs. If one SCR fails to commutate, the board’s dv/dt comparator flags “SHVI FAULT” within 2 µs and the Mark V blocks the next pulse—saving you from a diode explosion and a week-long outage. Bottom line: without the SHVI you can’t safely close the 2 kV gap between silicon and software.
Installation & Maintenance Pitfalls (Expert Tips)
Fiber bend radius is 1.5 in—no exceptions
Sharp kinks add 3 dB loss; the gate driver sees 8 mA instead of 15 and misfires. Use the orange plastic guide riveted to the bulkhead and zip-tie every 6 in.
Fiber bend radius is 1.5 in—no exceptions
Sharp kinks add 3 dB loss; the gate driver sees 8 mA instead of 15 and misfires. Use the orange plastic guide riveted to the bulkhead and zip-tie every 6 in.
Bayonet HV connectors must click twice
These carry 3 kV. A half-latch arcs, carbon-tracks the insulator, and you’ll chase “SHVI OVER-V” trips that clear when you open the door. Twist until you feel the second detent, then tug-test.
These carry 3 kV. A half-latch arcs, carbon-tracks the insulator, and you’ll chase “SHVI OVER-V” trips that clear when you open the door. Twist until you feel the second detent, then tug-test.
Differential feedback screws love to back out
Vibration loosens the 4-40 screws on J3/J4; resistance climbs, feedback droops, and the SDCC thinks current is low—so it over-fires and cooks the motor. Hit every screw 10 in-lb and re-torque after the first thermal cycle.
Vibration loosens the 4-40 screws on J3/J4; resistance climbs, feedback droops, and the SDCC thinks current is low—so it over-fires and cooks the motor. Hit every screw 10 in-lb and re-torque after the first thermal cycle.
Snubber resistors run 150 °C—don’t touch
The 100 Ω / 50 W ceramic blocks are live at bridge potential. Let the board cool five minutes before you swap it or you’ll get a 3 kV surprise through the wrist-strap.
The 100 Ω / 50 W ceramic blocks are live at bridge potential. Let the board cool five minutes before you swap it or you’ll get a 3 kV surprise through the wrist-strap.
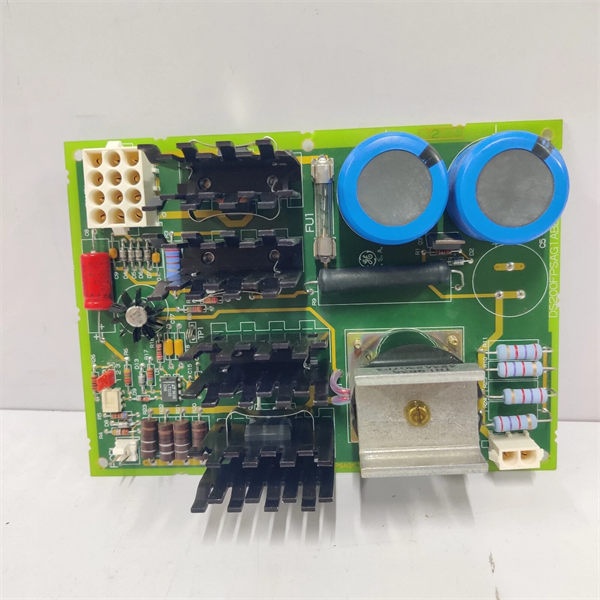

DS200FPSAG1ABB
Technical Deep Dive & Overview
DS200TBQDG1AFE is a passive-optical hybrid. Six Avago HFBR-1522 transmitters convert 5 V CMOS from the SDCC into 820 nm light pulses; receivers on each SCR gate-quench convert back to 15 V gate current. High-voltage feedback is scaled through precision 0.1 % dividers and delivered differentially to the SDCC A/D. RC snubbers (0.1 µF / 100 Ω) across each bridge arm limit dv/dt to <500 V/µs. No processor on-board—everything is hardware—so you can hot-swap with the bridge powered; the SDCC re-syncs gate pulses within 50 ms.
DS200TBQDG1AFE is a passive-optical hybrid. Six Avago HFBR-1522 transmitters convert 5 V CMOS from the SDCC into 820 nm light pulses; receivers on each SCR gate-quench convert back to 15 V gate current. High-voltage feedback is scaled through precision 0.1 % dividers and delivered differentially to the SDCC A/D. RC snubbers (0.1 µF / 100 Ω) across each bridge arm limit dv/dt to <500 V/µs. No processor on-board—everything is hardware—so you can hot-swap with the bridge powered; the SDCC re-syncs gate pulses within 50 ms.