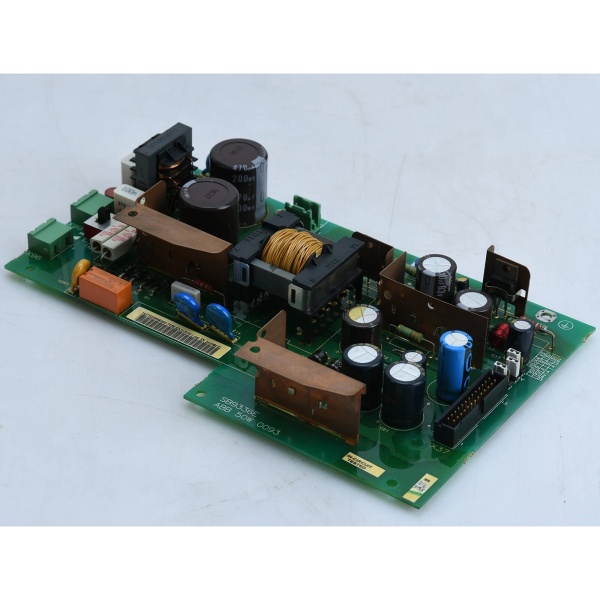
Description
Key Technical Specifications
- Model Number: SDCS-POW-1C
- Manufacturer: ABB
- Input Voltage: AC 115V/230V (field-selectable)
- Output Voltage: ±5V, ±15V, 24V DC (isolated channels)
- Output Voltage Stability: ±1% (full load range)
- Isolation Rating: 1500V AC (input-to-output, output-to-output)
- Operating Temperature Range: -25°C to +70°C
- Protection Functions: Overvoltage, undervoltage, overload, overheat, short circuit
- Power Conversion Technology: High-efficiency switch-mode design
- Compatibility: ABB DCS500/600 DC drive systems
- Certifications: IEC 61800-3, CE, UL, cUL
- Maintenance Feature: Supported hot swap (select system configurations only)

Field Application & Problem Solved
In harsh industrial environments like steel mills, paper plants, and mining operations, DC drive systems face two critical power-related challenges: unstable grid voltage and severe electromagnetic interference (EMI) from adjacent heavy machinery. These issues cause control circuit voltage fluctuations, leading to drive misfiring, unexpected shutdowns, or permanent damage to logic boards—costing plants hours of downtime and thousands in lost production. This is where the power module proves indispensable.
You will find this module in every DCS500/600-based system powering rolling mill drives, paper machine line motors, and mine hoist DC drives. Its core value lies in delivering isolated, low-ripple DC power to sensitive control components. The ±1% voltage stability eliminates logic errors caused by voltage swings, while the 1500V isolation blocks EMI cross-talk between power and control circuits. Additionally, the integrated soft start/stop logic syncs with the drive system to reduce inrush current during startup, preventing mechanical shock to motors and gearboxes and extending equipment lifespan.
For maintenance teams, the module’s multi-layer protection cuts down on troubleshooting time. Instead of chasing intermittent control faults, the module triggers clear alarms for overvoltage or overheat conditions, letting technicians address root causes—such as grid surges or blocked ventilation—before a full system failure occurs.
Installation & Maintenance Pitfalls (Expert Tips)
Input Voltage Selection is Non-Negotiable
Rookies often skip verifying the AC input voltage setting before powering on. The module has a physical selector for 115V/230V—set it wrong, and you’ll fry the internal inverter within seconds. In the field, always confirm the plant’s line voltage first; don’t rely on “standard” 230V assumptions, especially in older facilities with mixed voltage systems.
Improper Shield Grounding Kills Performance
While the module has robust isolation, poor shield grounding on input/output cables introduces EMI that causes output voltage ripple. This leads to intermittent drive faults that are impossible to trace with a multimeter. The fix: use a single-point grounding scheme for all cable shields, connected to the drive system’s main ground bus—not a random chassis point.
Capacitor Aging is a Silent Failure Point
Electrolytic filter capacitors degrade over time, especially in high-temperature plant environments. Aged capacitors cause output voltage instability and trigger false undervoltage alarms. Unlike overt faults, this issue creeps up gradually. My rule: replace capacitors every 5 years, even if the module passes a voltage test—this prevents unplanned shutdowns during peak production shifts.
Hot Swap Requires Pre-Check
The module is listed as “hot-swappable” in the manual, but this only works in systems with redundant power configurations. Rookies yank the module from non-redundant drives while the system is running, causing backplane arcing that damages the drive’s main interface board. Always check the drive’s power redundancy setting before attempting a hot swap.

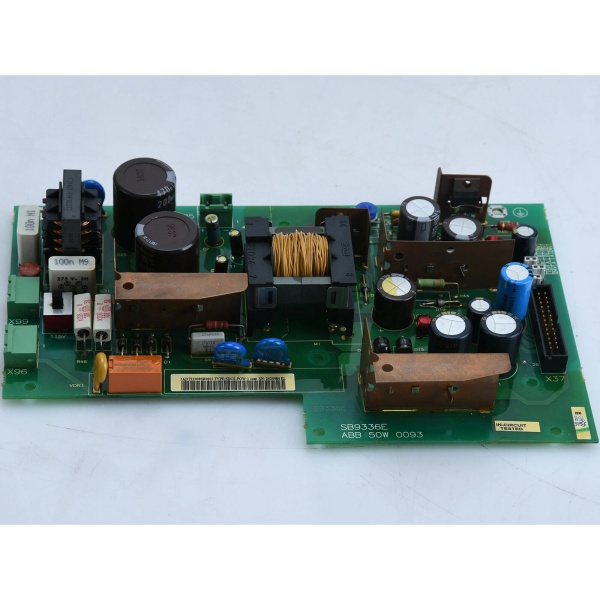
ABB SDCS-POW-1C
Technical Deep Dive & Overview
The module is a compact switch-mode power supply (SMPS) designed exclusively for ABB’s DCS500/600 DC drive architecture. It converts incoming AC 115/230V power into regulated, isolated DC outputs via a three-stage process: first, AC input is rectified and filtered into a high-voltage DC bus; next, a high-frequency inverter converts this DC bus into a low-voltage AC signal; finally, the AC signal is rectified again and filtered to produce clean ±5V, ±15V, and 24V DC power for the drive’s control stack.
A built-in feedback loop continuously monitors output voltage and adjusts the inverter’s duty cycle to maintain ±1% stability, even under full load or input voltage fluctuations. The soft start/stop logic interfaces with the drive’s main control unit to ramp power up/down gradually, eliminating inrush current spikes that stress both the module and connected motors. Integrated protection circuits use current and temperature sensors to trigger rapid shutdown or alarm signals—acting as a first line of defense for the drive’s expensive control electronics. The module communicates with the drive’s diagnostic system via the backplane, providing real-time status data for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance.





