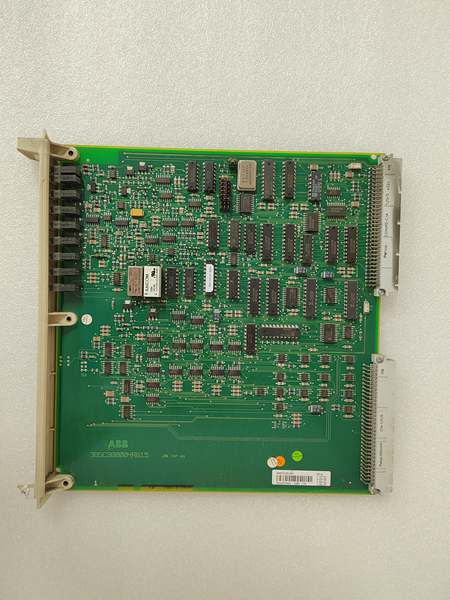
Description
Key Technical Specifications
- Model Number: ABB DSBC176 3BSE019216R1
- Manufacturer: ABB
- Fieldbus Protocol: Profibus DP V1 (EN 50170)
- Operating Modes: Profibus DP Master, Profibus DP Slave (software-configurable)
- Baud Rate Range: 9.6 kbps to 12 Mbps (auto-negotiation support)
- Max Connected Devices: 124 slaves (as master), 1 master (as slave)
- Operating Temperature: -25°C to 70°C (-13°F to 158°F)
- Storage Temperature: -40°C to 85°C (-40°F to 185°F)
- Isolation: 1kV AC (bus interface to backplane, 1-minute withstand)
- Transmission Distance: Up to 1000 meters (9.6 kbps), 100 meters (12 Mbps)
- Power Supply: 24V DC ±10% (21.6V DC to 26.4V DC), from AC 800M backplane
- Power Consumption: 1.5W (standby), 2.8W (full load)
- Mounting: AC 800M I/O rack (compatible with PM850/PM860/PM861/PM865 CPUs)
- Connector Type: 9-pin D-sub (female) + spring-cage terminal block (for bus lines)
- Protection Features: ESD protection (±15kV air), surge protection (±2kV), short-circuit protection on bus lines
- Compatibility: ABB AC 800M controllers (firmware ≥4.0)
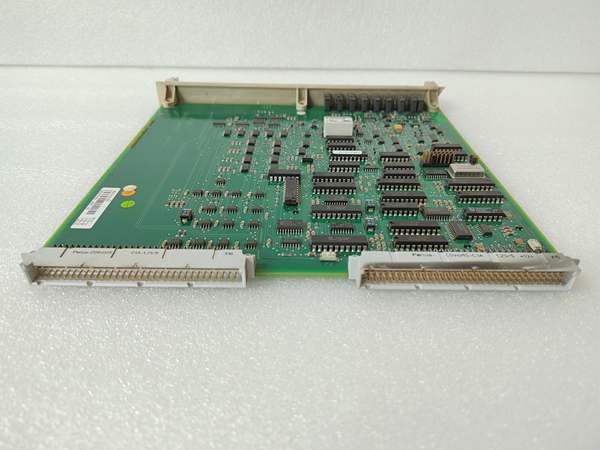

ABB DSBC176 3BSE019216R1
Field Application & Problem Solved
In industrial automation—refineries, automotive plants, and manufacturing facilities—Profibus DP remains a widely used fieldbus for connecting distributed I/O, drives, and sensors. The challenge? Integrating these Profibus devices with modern AC 800M PLCs requires reliable protocol translation that avoids data loss or latency. Many basic communication modules lack Profibus DP V1 support, limiting compatibility with advanced devices (e.g., intelligent drives with diagnostic data). Low-cost modules often skip galvanic isolation, causing noise-induced communication drops in harsh electromagnetic environments. Third-party modules struggle with AC 800M backplane synchronization, leading to inconsistent data transfer that disrupts control logic. The ABB DSBC176 solves these pain points with full Profibus DP V1 compliance, robust isolation, and native AC 800M integration.
You’ll typically find this module in applications like linking Profibus DP distributed I/O racks to AC 800M controllers in automotive assembly lines, integrating Profibus-enabled variable-speed drives in pulp mills, or connecting pressure/temperature transmitters to PLCs in chemical plants. It’s a staple in brownfield upgrades, where it preserves existing Profibus infrastructure while enabling integration with modern control systems—eliminating costly device replacements. In large-scale facilities (e.g., oil refineries), it acts as a Profibus master to coordinate dozens of slave devices across long distances, relying on its wide baud rate range to balance speed and transmission length. It also excels in multi-fieldbus environments, where it bridges Profibus DP networks with the AC 800M backplane for centralized control.
Its core value is seamless Profibus integration and network reliability. Profibus DP V1 support ensures compatibility with legacy and advanced devices alike, while galvanic isolation blocks noise and voltage transients. For operators, this means extended life for existing Profibus infrastructure, reduced capital costs, and reliable data transfer—critical in industries where replacing fieldbus systems is disruptive and expensive.
Installation & Maintenance Pitfalls (Expert Tips)
- Bus Topology Errors (Star Wiring = Signal Reflections): Rookies often use star topology (all devices connected directly to the module) instead of the required linear bus topology for Profibus DP. This causes signal reflections, leading to communication timeouts and data corruption. Install a linear daisy-chain: connect the first slave to the module, the second to the first, and so on. Avoid branching wires—use a bus coupler if additional branches are necessary.
- Termination Resistor Neglect (Missing = Signal Degradation): Profibus DP requires 120Ω termination resistors at the two ends of the bus, but rookies often omit them or install them in the middle. This leads to signal reflections and intermittent communication. Install a resistor at the module’s Profibus port and the last slave device in the chain. Verify with a multimeter—measure between the A and B lines; a properly terminated bus shows ~120Ω.
- Baud Rate Mismatch (Inconsistent Settings = No Communication): The module and all Profibus slaves must use the same baud rate, but rookies often mix settings (e.g., module at 1.5 Mbps, slave at 9600 kbps). This results in garbled data or complete communication failure. Document all slave baud rates first, then configure the module via Control Builder M to match. Use a Profibus analyzer to verify bus traffic and identify mismatched devices.
- Grounding Improperly (Shared Ground = Noise): Galvanic isolation protects the module, but rookies often connect the Profibus bus ground to different ground points than the AC 800M system. This creates ground loops, introducing noise that corrupts data. Connect the module’s Profibus ground terminal to the same system ground as the AC 800M controller. Use shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable for the bus, and ground the shield at one end (preferably the module) to avoid loop formation.
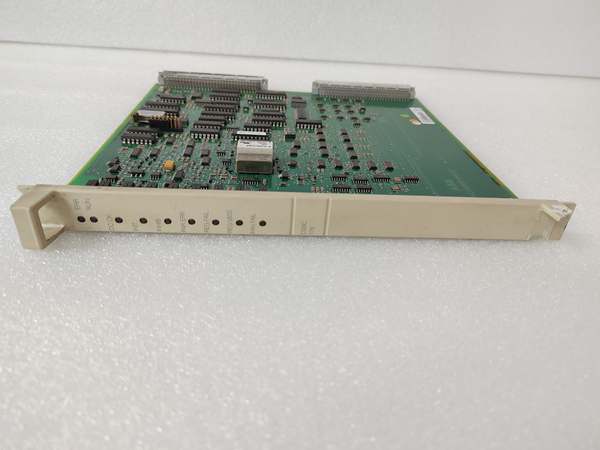

ABB DSBC176 3BSE019216R1
Technical Deep Dive & Overview
The ABB DSBC176 3BSE019216R1 is a Profibus DP communication module engineered to bridge Profibus DP field devices with ABB’s AC 800M control systems. Its core design centers on a dedicated Profibus DP V1 protocol processor that handles frame encoding/decoding, reducing the AC 800M CPU’s communication load. The module supports both master and slave modes, offering flexibility to integrate the AC 800M as a controller (master) or a data provider (slave) in Profibus networks.
Galvanic isolation (1kV AC) between the Profibus bus interface and the AC 800M backplane is a key design feature. This isolation blocks electromagnetic interference (EMI) from motors, transformers, and high-voltage equipment—common in industrial environments—and prevents voltage transients from damaging the controller. Surge (±2kV) and ESD (±15kV) protection further enhance durability against wiring mistakes and environmental stress.
Communication with the AC 800M CPU occurs via the rack’s high-speed backplane bus (100Mbps), enabling real-time transfer of Profibus data. The module’s internal memory caches process data objects (PDOs) and service data objects (SDOs), updating the CPU at intervals aligned with bus traffic. Baud rates (9.6 kbps to 12 Mbps) are configurable via Control Builder M, with auto-negotiation support to simplify setup.
Built for industrial ruggedness, the DSBC176 withstands vibration (up to 5g at 10-2000Hz) and temperature extremes (-25°C to 70°C). The 9-pin D-sub and spring-cage terminals simplify bus wiring, while the module’s compact 1-slot design maximizes I/O density in AC 800M racks. Compliance with Profibus DP V1 (EN 50170) ensures compatibility with thousands of industrial devices, from distributed I/O to intelligent drives.
As an OEM module, it integrates seamlessly with ABB’s Control Builder M software, supporting drag-and-drop configuration of Profibus master/slave parameters, slave device mapping, and diagnostic monitoring. Its focus on Profibus compliance, isolation, and reliability makes it a critical component for preserving legacy fieldbus infrastructure while enabling modern control system integration.